Poland: State of tunnelling works
source: Government release for GDDKiA (General Directorate for National Roads and Motorways) in Polish.
Tunnels on the roads on the board of GDDKiA - state of implementation
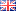
From December 2021, we gave to traffic on our road network tunnels with a total length of nearly 8.2 km. There are 9 km long facilities, and we have another 7.1 km in preparation. After they are built on the national road network, 18 tunnels with a total length of almost 25 km will operate on the GDDKiA network.
The oldest object is a single-bore tunnel, the only one with such a cross -section (the others are twelve), on the S1 expressway in Laliki, commissioned in 2010. The latest are two short tunnels along the S52 Northern Krakow beltway, 653 and 496 m long, made available to movement in December last year. The title of the longest tunnel is currently entitled to the object along S2 in Warsaw's Ursynów (with three lanes and reserve to the fourth), which is 2335 m long between the eastern and western portal. However, it is dethroned by an object passing 40 meters below the measles mirror, which will be built on S6 along the western beltway of Szczecin, 5003 m long. The Warsaw tunnel will fall to third place, giving way to an object with a length of 2910 m, which will pass under the Kamieniec hill in the Dynów Foothills, on the S19 Jawornik - Lutcza section in the voivodeship. Podkarpackie. For many years, however, he will be a leader in terms of traffic. The tunnel section of the southern bypass of Warsaw, since its opening in December 2021, has already traveled over 90 million vehicles, on average over 80 thousand. during the day.
The first tunnel, in Laliki on S1 (Silesian Voivodeship), is 678 m long and was hollowed out in the mining method in NATM (New Austrian Tunnelling Method) in the Sobczakowa Graph Massif. In the same technology, a tunnel on the S3 Bolków - Kamienna Góra, with a length of 2300 m in the vicinity of Stare Bogaczowice, as well as two objects along the S1 at the circumvent of Węgierska Górka was created. The shorter, measuring approx. 820 m, is drilled in the massif of the Barania Góra, and the longer - about 980 m - under the Białożyński group. We will be able to take advantage of both tunnels, as well as the entire, nearly 9-kilometer route between Przybędza and Milówka nodes this year.
In a nutshell, tunnel drilling with the mining method involves drilling in rock, by specialized machines, a number of holes to which explosives are then introduced. After their detonation, the crushed rock is removed and the walls of the tunnel stabilized. In NATM technology, or the "new Austrian method", the tunnel is drilled with short sections, and the walls of the tunnel strengthening are a layer of spray concrete (torcret) and rock anchors or steel ribs. The mining method, but in ADECO-RS (Analysis of Controlled Deformations in Rocks and Soils), i.e. control of displacements and deformations in the rocks and soil, which is the development of NATM, a tunnel for S7 repair was performed-White rock. This method is used for drilling in difficult geological conditions, and such performers dealt with such performers in a 2058 m long facility passing through cracked Carpathian flysch near Luboń Mały.
In both technologies, after hollowing out the next section of the rocks and the initial enclosure of the tunnel, a basic housing was made inside it. After laying waterproofing and reinforcement, subsequent segments of the housing were concreted, using mobile formwork. In the tunnel in Zakopane we drive on a concrete surface of a paddler slab, under which there is a technological space. The concrete surface of the road, laid on the casing of the main tunnel and subsequent layers of the foundation, is in the already used tunnels on S3 and built on S1.
A shorter tunnel on S3, at Gostków, 320 m long, was created using the Cut & Cover opencast method, in an open excavation. His foundations were placed on a rock ground and a two -nave reinforced concrete frame was made. The tunnel structure consists of 27 segments, and the whole after proper insulation was buried again. Animals can move around the tunnel and access to fields was also provided.
... underpayable, with crevice walls ...
In turn, tunnels along S2 in Warsaw and S52 on the outskirts of Krakow were created using the sub -legged method. In the shallow excavation, the slot walls were first made of a dozen to several dozen meters deep into the ground, and then a thick reinforced concrete ceiling, from which the ground was then chosen between the slit walls. In the next stage, the bottom of the tunnel was concreted, subsequent structural layers of the road under the target concrete surface of the road and finished walls of the tunnel. These types of facilities are built at a small depth under ground level. The tunnel in Ursynów, however, had to go under the metro line, and one of the tunnels on the northern beltway of Krakow, in Zielonki, passes under the Prądnik Valley. In the same method, a tunnel is built, with a length of 317 m, along DK79 on the Zabierzów beltway near Krakow, and there will also be two tunnels along the northern S7 outlet in Warsaw with a length of 1000 and 1122 m.
... using the TBM machine
At the construction of a one -nave tunnel under the pig (this is the investment of the city of Świnoujście, where GDDKiA played the role of a substitute investor) the method of drilling with the TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine) machine was used. A large cylindrical machine with a rotating head, 13.5 m in diameter, with disc cutters broke from the island of Uznam at Wolin. The machine, breaking the ancestor of the tunnel, at the same time installed its housing, and then the evacuation outputs and the road under which the Evacuation Gallery were placed were made. The tunnel under the pig measures 1480 m in length and is managed by the city self -government.
The TBM machine that you called Karpatka drills the first nave of the tunnel along S19 Rzeszów - a Babica with a length of 2250 m. The shield of the 15.2 m diameter machine is working in the embarrassing Carpathian flysch, in which areas with escalating methane were detected, which caused later than the start of drilling. The TBM machine was prepared for work in methane conditions, and on January 30 this year. A 464 m tunnel under the Grochowiczna hill has already been made.
Mechanical mole, with a shield with a diameter below 15 m, will be carried out by the planned 5-kilometer tunnel under the Odra along the western beltway of Szczecin on S6. The use of TBM machines to hollow out two tunnels in the Dynów Foothills is declared by contractors of two sections of S19 in the province. Podkarpackie. It is about nearly 3 -kilometer under the Kamieniec hill on the section Jawornik - Lutcza and nearly a kilometer under the Hyb hill on the neighboring fragment of the route, Lutcza - Domaradz.
The systems supervise, process and react on a regular basis
In each of the already functioning tunnels, their users are supervised by numerous cameras and various sensors included in the safety and tunnel control system (such systems will also be built and planned). Each of the tunnels is illuminated, equipped with a fire detection and signaling system, a system of emergency points with phones connected with the Movement Management Center in the tunnel, also equipped with fire extinguishers and fire blankets. There are also evacuation transitions to the neighboring nave, and in Laliki to the parallel evacuation tunnel. Tunnel ventilation with normal movement is provided by air shoots caused by moving vehicles. This natural ventilation can be supported by mechanical, and its inclusion is determined by readings of the pollution measurement system (CO and NOX), air flow speed and visibility. The ventilation system is also responsible for safety during a fire, the supply of fresh air and the tunnel smoke out.
The television supervisory system has the function of automatic detection of specific events, e.g. the appearance of a pedestrian in the tunnel, stopping the vehicle or driving against the tide. Algorithms are able to identify, monitor and report situations and facilities that can be a potential risk of an accident or fire. In the event of a violation of safety rules, e.g. slowed or stopped vehicle traffic, driving against the tide or loss of load by any of the traffic participants or detecting the presence of smoke, alarms are automatically activated in the tunnel. Tunnel management center employees can use the camera and video system to recognize the threat, on the basis of which the decision will be made to confirm the fire alarm, e.g. when we are dealing with lots of smoke and a small amount of heat.
On the signs of the variable content before entering the tunnel there may be warnings about atmospheric conditions, about the bay in the tunnel, and if the entire tunnel is blocked, drivers will see information about detours on them. Some of the tunnels have a sectional speed measurement subject to the Road Transport Inspection.
Tunnels on the GDDKiA network
In use (seven with a total length of 8.8 km):
S7 Lubień - Rabka -Zdrój (Lesser Poland Voivodeship): 2058 m,
S2 Southern Warsaw bypass (Masovian Voivodeship): 2335 m,
S1 gray - Laliki (Silesian Voivodeship): 678 m,
S3 Bolków - Kamienna Góra (Dolnośląskie Voivodeship): 2300 and 320 m,
S52 Northern Krakow beltway (Lesser Poland Voivodeship): 653 and 496 m
DK93 in Świnoujście (West Pomeranian Voivodeship): 1485 m (maintained by the city self -government).
In implementation (eight with a total length of 9 km):
S1 Przybędza - Milówka (Śląskie Voivodeship): 980 and 820 m,
S19 Rzeszów - Babica (Podkarpackie Voivodeship): 2250 m,
S19 Jawornik - Domaradz (Podkarpackie Voivodeship): 2910 and 990 m,
S74 Kielce West - Kielce (Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship): 499 and 200 m,
DK79 Zabierzów (Lesser Poland Voivodeship): 317 m.
In preparation (three with a total length of 7.1 km):
S6 western beltway of Szczecin (West Pomeranian Voivodeship): 5003 m,
S7 Kiełpin - Warsaw (Masovian Voivodeship): 1122 and 1000 m.
cover tunnel photo by: Matt Brown from London, England / CC BY
Copyright 2019-2024 TunnelContact.com