Austrian researchers develop shotcrete mix-designs for tunnels with longer service-life
A team of researchers from Austrian Society for Construction Technology (ÖBV), TU Graz (Technical University of Graz) and OTH Regensburg have developed robust tunnel shotcrete mix-designs that would last longer.
Please find below the press release from TU Graz:
Sustainable shotcrete mix-designs for tunnels with longer service-life
11/16/2020 |
A project jointly initiated by the Austrian Society for Construction Technology (ÖBV), TU Graz and OTH Regensburg provides a more systematic understanding of shotcrete applications and forms the basis for new, even more durable concrete mixes and thus for more durable tunnels.
The service life of tunnels today is designed to last at least for one hundred years – in the case of the Brenner basis tunnel it is even 200 years. The problem with this: "The service life is currently calculated on the basis of theoretical key figures and empirical values. Environmental conditions such as chemically aggressive groundwater, for example, can possibly lead to cost-intensive maintenance measures earlier than expected," says Florian Mittermayr, researcher at the Institute of Technology and Testing of Construction Materials at Graz University of Technology.
Focus on new, fundamental knowledge about shotcrete
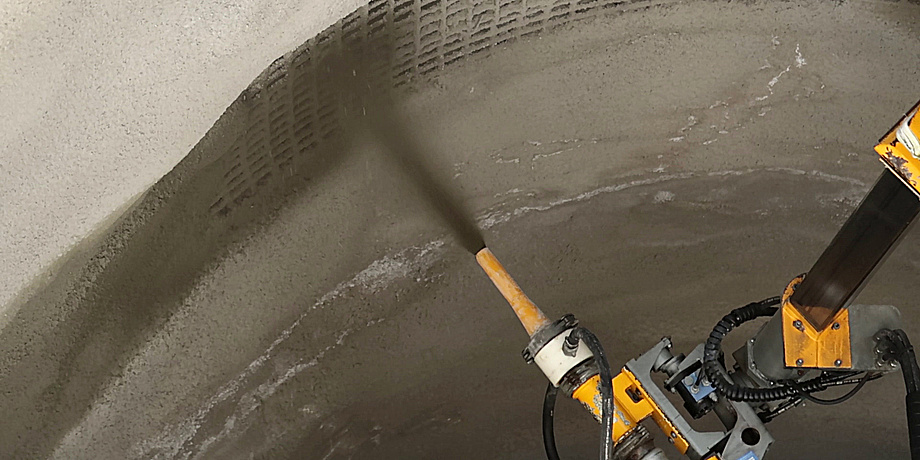
One of the most important support measures in tunnel construction is the use of shotcrete, also known as sprayed concrete. In this application, concrete is applied via a nozzle and, depending on requirements, admixtures are added. Mix-designs for shotcrete have so far been based on experience and practical knowledge. The findings of the research project should now provide basic data for precise and tailor-made durable mixes.
In order to find out how different shotcrete formulations interact with the environment, which formulations are best suited for which environmental influences and what effects additives have on durability and workability, Mittermayr initiated the "Advanced and Sustainable Sprayed Concrete (ASSpC) " research project together with Wolfgang Kusterle from the Concrete Laboratory of the OTH Regensburg and the Austrian Society for Construction Technology (ÖBV). "For four years, we investigated the process in its entirety in many laboratory and large-scale tests and provided scientific support at various tunnel construction sites," explains Mittermayr.
The researchers were able to unravel how shotcrete should ideally be processed and how binders must be constituted to achieve particularly high durability.
Optimized mix-design
One main finding is that shotcrete can be designed more durable when cements, supplementary cementitious materials, admixtures and aggregates are better matched to the requirements. Even small deviations in quantity can reduce the desired effect.
In the investigations it was proven that granulated blast furnace slag – in combination with other supplementary cementitious materials – is an effective way of increasing resistance against sulphate attack. Sulphate ions (N.B. usually caused by the dissolution of gypsum) can be present in soil or groundwater and lead to deformations and subsequently to cracks in the concrete. Supplementary cementitious materials such as metakaolin or siderite from the Styrian Erzberg help to reduce the contribution of shotcrete to sinter formations in the drainage system. In this context, sintering is referred to the process ofcalcium carbonate precipitation in the drainage pipes of tunnels. This can lead to clogging of the drainage system and is therefore a frequent reason for tunnel closures due to maintenance work.
In addition, even a small addition of ultrafine limestone powder can significantly increase the early strength of shotcrete. This effect makes it possible to use additives such as granulated blast furnace slag, metakaolin or siderite in larger quantities than is currently possible, making shotcrete not only more durable but also more sustainable.
Research transfer and open questions
The important questions for durable and sustainable shotcrete regarding constituent materials and mixtures and their interaction with the surrounding media were able to be clarified and deciphered, and the project partners are now preparing the detailed results for practical application. "Another milestone in terms of sustainability; we are particularly pleased about that. The extended service life means that tunnels can now be maintained at longer intervals, the maintenance effort is reduced for the operator and for motorists this means less congestion. Also impressive is the research zeal of the universities, which is helping to position our building material more and more as an environmentally friendly material with precise and tailor-made formulations," explains Sebastian Spaun, managing director of the Association of the Austrian Cement Industry (VÖZ), another important partner in the consortium.
For Michael Pauser, managing director of the Austrian Society for Construction Technology (ÖBV), "The ÖBV-FFG research project is one more proof that these newly investigated and in practice already tested concrete formulations make a further contribution to the climate protection goals. The cooperation between universities, clients and the construction and building materials industry ensures that the research is practice-oriented and its results will be incorporated into the shotcrete guideline of the Austrian Society for Construction Technology, which is known beyond Austria's borders."
Another important finding of the project is also the influence of shotcrete application technology. Any open questions and potential for improvement associated with this are to be investigated in a new research project and corresponding suggestions for improvement developed.
Cooperation of key players
The scientific consortium included researchers from the TU Graz Institutes of Applied Geosciences and of Technology and Testing of Construction Materials, the Concrete Laboratory of OTH Regensburg and the materials technology working group of the University of Innsbruck. The scientists were supported by "Austria's concentrated industrial shotcrete competence" (quoted by Kusterle).
This industry project submitted by the Austrian Society for Construction Technology (ÖBV) is being carried out in the framework of the Collective Research programme funded by Austrian Research Promotion Agency. The project results are available to the entire Austrian construction and concrete industry in line with the funding scheme.
Research at TU Graz is in the Fields of Expertise "Advanced Materials Science" and "Sustainable Systems", two of the five strategic research core areas of the University.
Source:
cover tunnel photo by: Matt Brown from London, England / CC BY
Copyright 2019-2024 TunnelContact.com









https://www.tugraz.at/en/tu-graz/services/news-stories/media-service/singleview/article/nachhaltigere-spritzbeton-rezepturen-fuer-laengere-nutzungsdauer-von-tunnel0/
Sustainable shotcrete mix-designs for tunnels with longer service-life
www.tugraz.atA project jointly initiated by the Austrian Society for Construction Technology (ÖBV), TU Graz and OTH Regensburg provides a more systematic understanding of shotcrete applications and forms the basis for new, even more durable concrete mixes and...